And although the aforementioned mistakes are typically easily remedied, in some cases, transposition errors relating to medicinal dosing information may lead to tragic consequences. For example, recording a payment meant for accounts payable in accounts receivable. These errors can distort the financial statements by misrepresenting the nature of transactions. While the trial balance may still tally, the financial statements will not accurately reflect the business’s activities. Implementing a robust chart of accounts https://www.bookstime.com/ and providing adequate training to accounting personnel can help reduce the incidence of commission errors. Regularly comparing account balances against external sources, such as bank statements, can reveal discrepancies that stem from transposition errors.

Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
- As well as being incorrect, these figures affect all subsequent entries made in the ledger.
- Entry reversal throws off the accuracy of your books and financial statements.
- For example, say you receive a bill for $450 that you accidentally enter as $540 in your accounting software.
- For example, if goods are purchased from Harry amounting to $500, which are wrongly replaced by Harry, it will not disturb the trial balance.
- By ensuring that different individuals are responsible for recording transactions, authorizing payments, and reconciling accounts, the likelihood of errors can be significantly reduced.
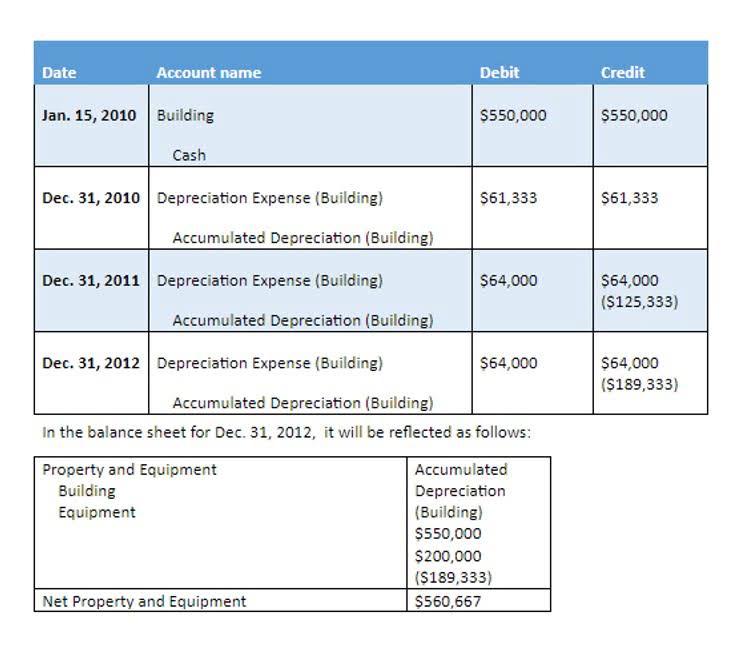
Reconciliation should be performed at consistent intervals to catch errors promptly, reducing the potential for compounded mistakes that can escalate over time. To mitigate the risk of transposition errors, organizations can implement a series of methodical checks and balances. One effective strategy is the use of double-entry accounting, a system where each transaction is entered twice, once as a debit and once as a credit. trial balance When material errors are discovered that affect previously issued financial statements, the company must determine the appropriate method of restatement. This typically involves revising the affected financial statements to reflect the correction of the error.
- And although the aforementioned mistakes are typically easily remedied, in some cases, transposition errors relating to medicinal dosing information may lead to tragic consequences.
- Additionally, transportation errors can lead to inaccurately-recorded customer profiles.
- Understanding how to address these discrepancies effectively is essential for upholding the integrity of financial information.
- The employee’s hourly rate is $21 per hour, but you accidentally enter $12.
Run your business with confidence

OK, so now let’s get back into the transposition mistake magic “9” identifier. If your discrepancy is evenly divisible by the number 9, you may have a transposition error on your hands. While creating the journal entry, you credit your Sales account $1,810.

Recording Error Corrections
The problem arises when an individual is unable to retain the correct order of digits in a calculation. These errors can result in catastrophic financial results, or in the death of a person. Transposition errors affect the aorta and pulmonary arteries, which are both major blood vessels that leave the heart. When this happens, the aorta begins in the right ventricle, while the pulmonary artery begins in the left ventricle. If syncing with apps has stopped, accounts don’t balance, or entries are miscategorized, it’s possible there’s been a misuse of accounting software.

Understanding Transpositional Errors
These errors can distort the financial health of a business, leading to inaccurate profit and loss statements. Regular audits and cross-referencing with original documents can help in identifying and correcting these discrepancies. Ensuring that employees are well-trained and that there are robust internal controls in place can significantly reduce the occurrence of posting errors. Once errors in the trial balance have transposition error been identified, the next step is to correct them to ensure the accuracy of financial statements. The process begins with a thorough investigation to understand the nature and cause of each error. This often involves revisiting the original transaction documents, such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements, to verify the correct amounts and accounts.